Architecting a Real time Streaming Deep Learning Text Classification Pipeline With Python¶
The client startup company wants to retweet all AI tweets which has links in them, they think doing so will attract more followers to their handle.
Requirements¶
Refer the following link for general architecture of our continuous integration ML pipeline theory on Architecting a Machine Learning Pipeline
Create a pipeline similar to following illustration
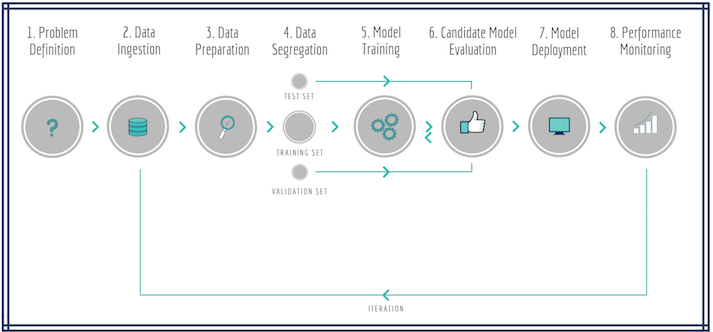
Build ground up dataset for tweet classification (AI tweet or not) using the live streaming data
Dump the raw tweet data into a table in Postgresql DB called
streamingdbHave configuration to prefix the name of the raw tweet data and version config to dump the tables into DB
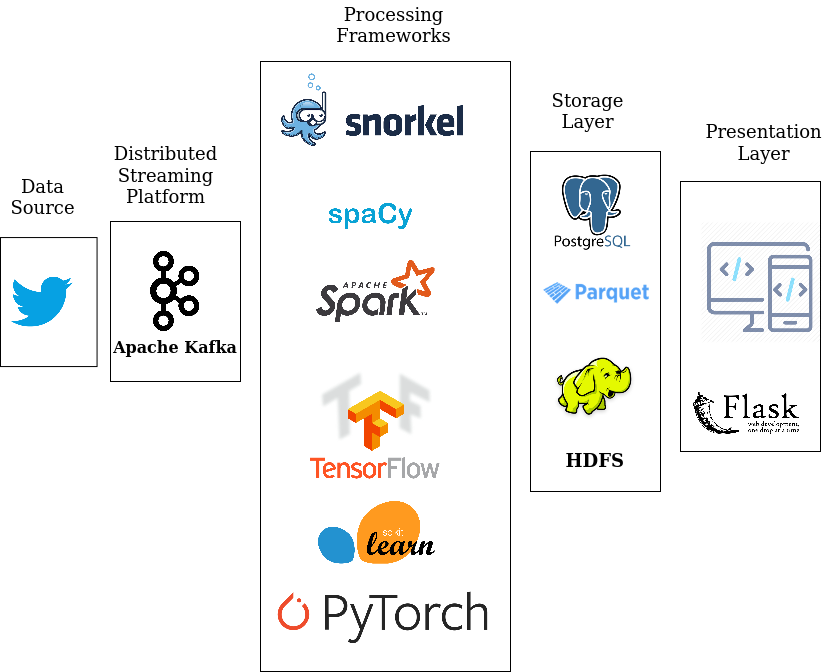
Use semi supervised methods to tag dataset, for example frameworks like [https://www.snorkel.org/](https://www.snorkel.org/
Build a UI tool to annotate the semi supervised tagged data to create golden dataset for ML training
Build a Naive Deep Learning/ Neural network model and evaluate it on golden/sem supervised dataset
Deploy the model, classify the text
Extract the web links from tweets and store the urls
Implementation¶
Problem Definition
Build a modular streaming ML/DL pipeline
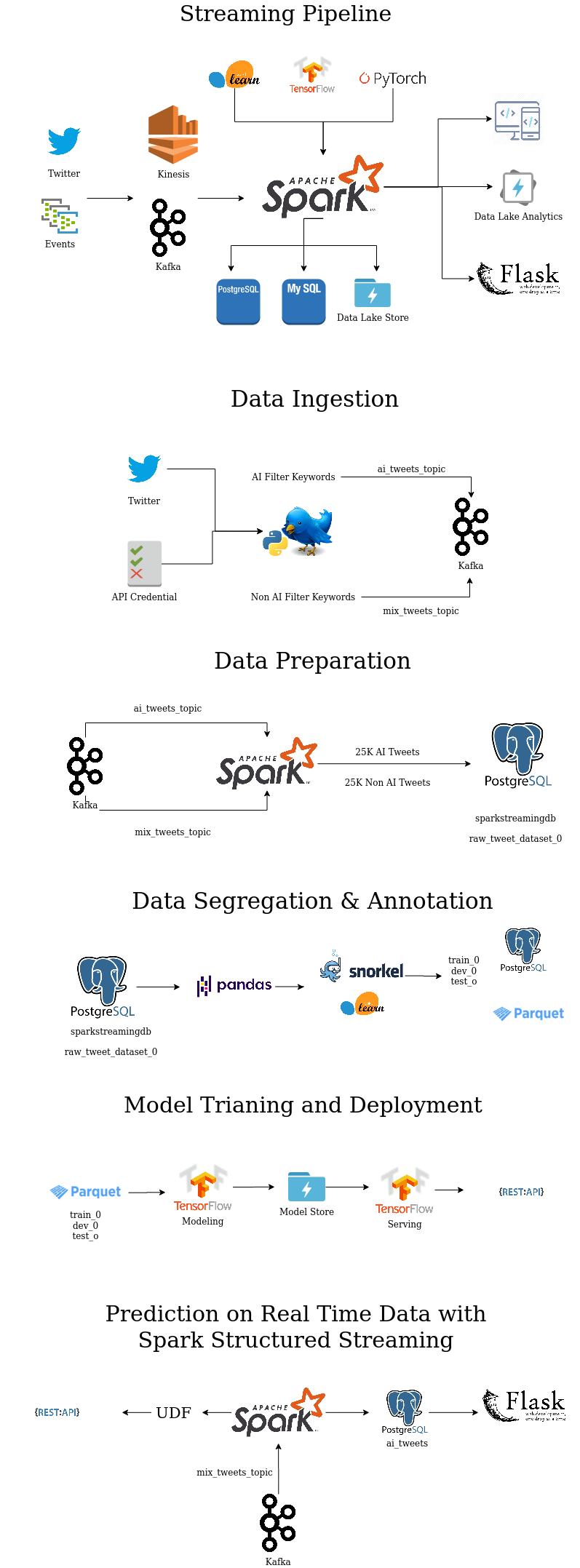
Data Ingestion / Data Collection:
Tweets ---> Twitter Stream ---> Tweepy ---> Kafka Producer ---> Kafka Stream -- -> Spark Structured Streaming Consumer ---> Postgresql as one single raw data table
Data Preparation / Data Labelling and Segregation
Posgresql ---> Raw Dataset Table ---> Split ---> Train/Test/Dev/Snorkel dataset tables -- -> SSPLabeler(Snorkel Labeler) -- -> Labelled Train/Test/Dev dataset stored in Postgresql & Disk Labelled Train/Test/Dev dataset on Posgresql---> Mannual UI Tagger -- -> Train/Test/Dev dataset with golden label column on PosgresqlModel Training and Evaluation
Labelled Train/Test/Dev dataset ---> DL Model ---> Model Store
Deployment / Prediction on Live Stream
Model Store ---> Tensorflow Serving ---> TF API End Point Tweets ---> Twitter Stream ---> Tweepy ---> Kafka Producer ---> Kafka Stream -- -> Spark Structured Streaming Consumer ---> UDF(TF API End Point) -- -> Filtered AI Tweets ---> PostgresqlMonitoring / Dashboard
Postgresql ---> Flask API ---> Dashboard
Dataset tables:
Tables are suffixed with
run/version idstarting from0, refer respective bin/*.sh files for version configurations
| Table Name | Records | Info |
|---|---|---|
| raw_tweet_dataset_0 | 50K+ | Full Raw Dataset |
| deduplicated_raw_tweet_dataset_0 | ~ | Depulicated on text column |
| test_dataset_0 | 1000 | Test dataset |
| dev_dataset_0 | 500 | Dev dataset |
| snorkel_train_dataset_0 | 10K | Snorkel train dataset |
| train_dataset_0 | ~ | Model train dataset |
Configuration¶
How to run?¶
There are two ways of running, that is on docker or on your local machine. In either case, opening the terminal is the difference, once the terminal is launched, the steps are common.
Start the docker container, if needed:
docker run -v $(pwd):/host/ --hostname=$(hostname) -p 50075:50075 -p 50070:50070 -p 8020:8020 -p 2181:2181 -p 9870:9870 -p 9000:9000 -p 8088:8088 -p 10000:10000 -p 7077:7077 -p 10001:10001 -p 8080:8080 -p 9092:9092 -it sparkstructuredstreaming-pg:latest
To get a new terminal for our docker instance run : docker exec -it $(docker ps | grep sparkstructuredstreaming-pg | cut -d' ' -f1) bash
Note: We pull our container run id with $(docker ps | grep sparkstructuredstreaming-pg | cut -d' ' -f1)
This example needs multiple terminals:
On each terminal move to the source root folder:
# Local machine cd /path/to/spark-streaming-playground/ # On Docker 'spark-streaming-playground' is mountes as a volume at /host/ cd /host export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd)/src/:$PYTHONPATH
Data collection
There can be of two ways
First and easy way is use the dump as part of this repo
export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd)/src/:$PYTHONPATH python src/ssp/posgress/dataset_base.py --mode=upload
Second way is dumping data from live stream, which may take few hours depending up on the frequency of the AI/ML/Big Data tweets
#[producer] Guake terminal name! vim bin/data/start_kafka_producer.sh bin/data/start_kafka_producer.sh #[dump data] #by default 50K tweets (25K AI tweets + 25K False positive) will be collected and dumbed into the table vim bin/data/dump_raw_data_into_postgresql.sh bin/data/dump_raw_data_into_postgresql.shData preparation for model training, with default snorkel labeller
#[ssp data] # check the version points to the one we wanted, to begin with it has to be 0 # --mode switch has two options: 'split' for crating the train/test set from initial full data table and # 'download' to dump the labelled data, same outpath is used expect it is annotated with '_labelled' vim bin/data/prepare_ssp_dataset.sh vim config/default_ssp_config.gin # check for `SSPMLDataset` params bin/data/prepare_ssp_dataset.shSnorkell Label Function coverage will be printed as part of the logs, as follows:
j Polarity Coverage Overlaps Conflicts is_ai_tweet 0 [1] 0.3125 0.0587 0.0587 is_not_ai_tweet 1 [0] 0.3469 0.1597 0.0000 not_data_science 2 [0] 0.1084 0.0983 0.0482 not_neural_network 3 [0] 0.0036 0.0030 0.0030 not_big_data 4 [0] 0.1133 0.1048 0.0057 not_nlp 5 [0] 0.0132 0.0120 0.0004 not_ai 6 [0] 0.0084 0.0067 0.0059 not_cv 7 [0] 0.0081 0.0068 0.0016
Mannual tagger
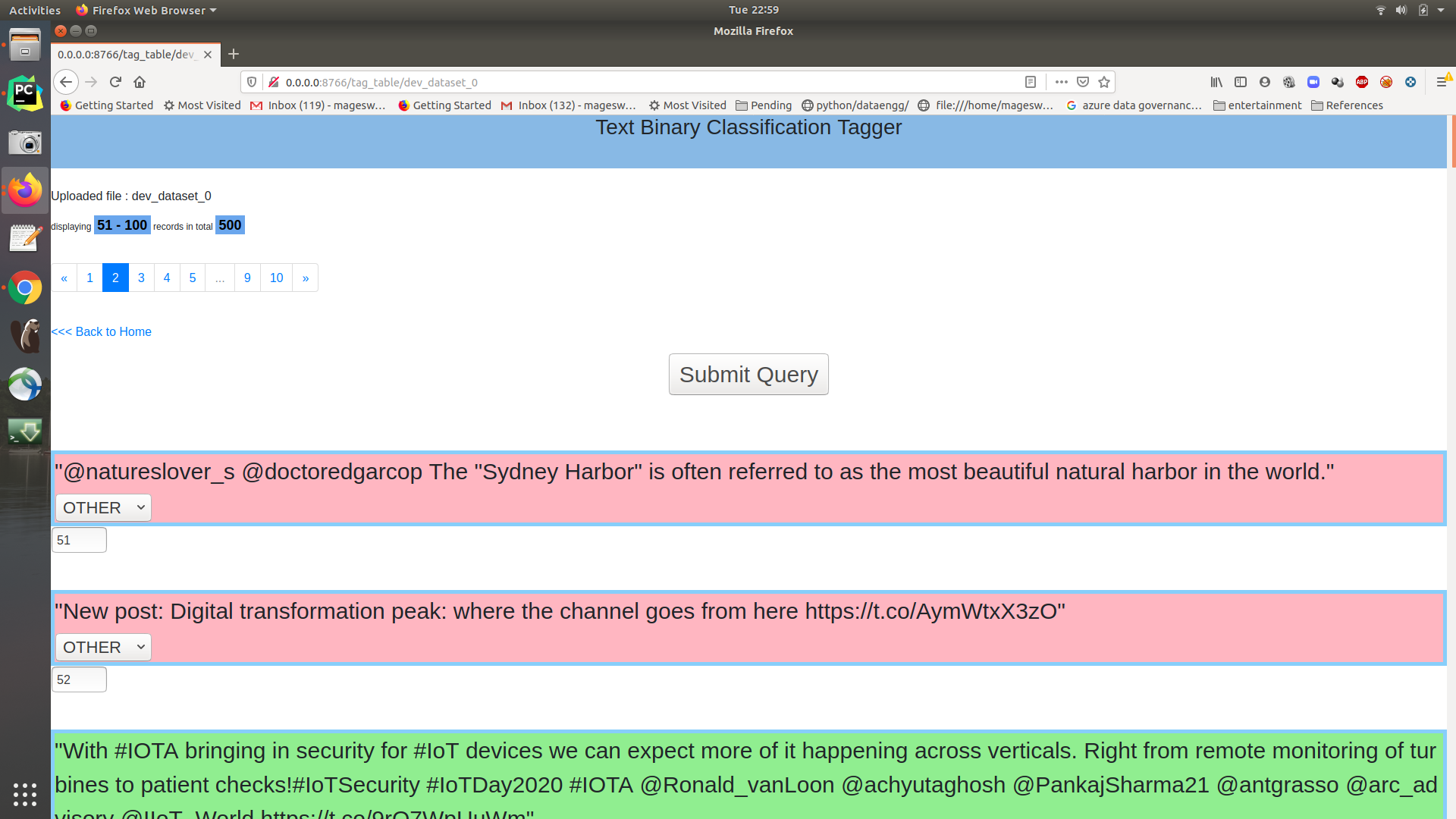
#[tagger] bin/flask/tagger.shEvalaute the Snorkel labeller with respect to hand labels
#[snorkell] vim bin/models/evalaute_snorkel_labeller.sh bin/models/evalaute_snorkel_labeller.shTrain Deep Learning model
#[DL Text classification Model] vim config/default_ssp_config.gin #check the paths in NaiveTextClassifier params bin/models/build_naive_dl_text_classifier.shStart Tensorflow Serving
Through installation
#[Tensorflow Serving] # give appropriate model path that needs to be served export MODEL_DIR=/home/mageswarand/ssp/model/raw_tweet_dataset_0/naive_text_classifier/exported/ # test the model saved_model_cli show --dir ${MODEL_DIR}/1/ --all # start the serving server tensorflow_model_server \ --rest_api_port=8501 \ --model_name="naive_text_clf" \ --model_base_path="${MODEL_DIR}"Through docker
# Download the TensorFlow Serving Docker image and repo docker pull tensorflow/serving export MODEL_DIR=/home/mageswarand/ssp/model/raw_tweet_dataset_0/naive_text_classifier/exported/ docker run -p 8501:8501 \ --mount type=bind,source=${MODEL_DIR},target=/models/naive_text_clf \ -e MODEL_NAME=naive_text_clf -t tensorflow/servingThrough Kubernetes, using local machine as driver (TODO: try creating a private cluster with docker as driver)
you may have delete previous minikube driver
minikube stop minikube delete
Start minikube
sudo minikube start --vm-driver=none #--cpus=6 --memory=16000mb # this will take few mins #eval $(minikube docker-env) #export DOCKER_CERT_PATH=${HOME}/.minikube/certs #bug fixGet the default tensorflow serving docker image
docker pull tensorflow/serving # Make sure the port 8501 is free and not used by any application sudo netstat -tulpen | grep 8501 #you should see blank output
Prepare a new serving image with the model
#Start the default tensorflow serving docker image with a name "serving_base" docker run -d --name serving_base tensorflow/serving export MODEL_DIR=/home/mageswarand/ssp/model/raw_tweet_dataset_0/naive_text_classifier/exported/ # copy the model artifacts docker cp ${MODEL_DIR} serving_base:/models/naive_text_clf # save the image with the model docker commit --change "ENV MODEL_NAME naive_text_clf" serving_base naive-text-clf-serving # kill and remove the default image docker kill serving_base docker rm serving_baseTest the image
# Run the image and test APIs are working fine # run below test script: tensorflow_serving_api_udf.py # after testing kill the docker image, jus make sure there are no multiple docker images running docker inspect $(docker ps | grep naive-text-clf-serving | cut -d' ' -f1) docker kill $(docker ps | grep naive-text-clf-serving | cut -d' ' -f1)Create kubernetes deployment and service pods
kubectl create -f kubernetes/tensorflow_naive_classifier.yaml sudo netstat -tulpen | grep 30125 kubectl get pods kubectl get deployments kubectl get services kubectl describe service naive-text-clf-service
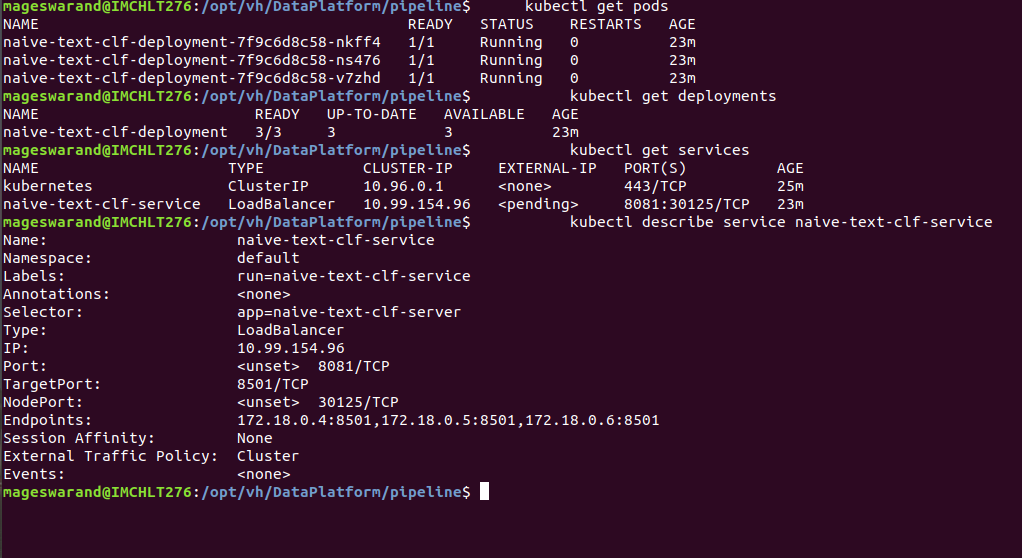
Delete the kubernetes service cluster
# if you wanted to clear out all the kubernetes stuff kubectl delete -f kubernetes/tensorflow_naive_classifier.yaml
Test the serving REST end point
export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd)/src/:$PYTHONPATH python src/ssp/spark/udf/tensorflow_serving_api_udf.py
Start live Spark streaming for AI/Data Science tweet classification
# [Spark Streaming] bin/nlp/spark_dl_text_classification_main.shStart the AI Tweets dash board
[dashboard] bin/flask/ai_tweets_dashboard.sh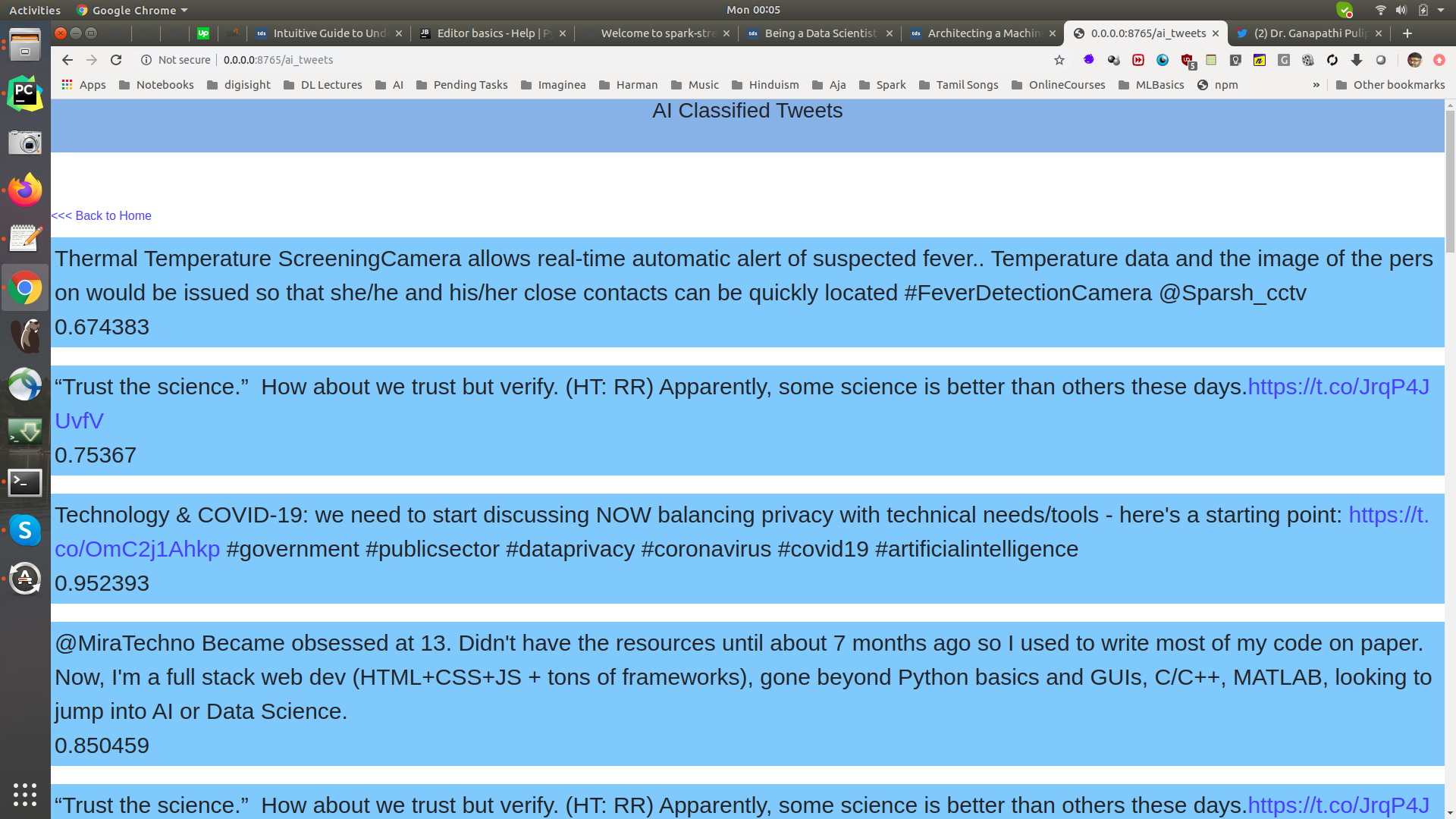 A Flask Web UI with the text and its prediction probability!
A Flask Web UI with the text and its prediction probability!Clean all Postgresql DB tables
DROP SCHEMA public CASCADE;
CREATE SCHEMA public AUTHORIZATION sparkstreaming;
GRANT ALL ON schema public TO sparkstreaming;
Take Aways / Learning’s¶
TODOs
Medium post on the use case @ https://medium.com/@mageswaran1989/big-data-play-ground-for-engineers-architecting-a-realtime-streaming-deep-learning-pipeline-with-c0305407f21d
References
- https://towardsdatascience.com/deploy-your-machine-learning-models-with-tensorflow-serving-and-kubernetes-9d9e78e569db
- https://towardsdatascience.com/custom-transformers-and-ml-data-pipelines-with-python-20ea2a7adb65
- https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-build-a-complex-reporting-dashboard-using-dash-and-plotl-4f4257c18a7f
- https://github.com/ucg8j/awesome-dash
- https://github.com/tensorflow/serving
- https://github.com/tensorflow/serving/blob/master/tensorflow